| HYDROGENATED BISPHENOL A | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 80-04-6; 71402-84-1; 93882-53-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 201-244-2 | |
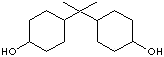
| FORMULA | (CH3)2C(C6H10OH)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 240.38 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 4,4'-(1-Methylethylidene)biscyclohexanol; | |
| 1,1'-Isopropylidenebis(4-cyclohexanol); 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)propane; 4,4'-Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol; Dodecahydrobisphenol A; HBPA; 4-[2-(4-Hydroxycyclohexyl)propan-2-yl]cyclohexan-1-ol; | ||
| DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white flakes | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | 253 - 257 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 194 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Bisphenol-A structure is a key difunctional building block to important polymers and polymer additives. Bisphenol A is also used as an antioxidant in plasticizers and as a polymerization inhibitor. Hydrogenated Bisphenol-A is used as co-monomers in polymerization to form thermosetting epoxide polymer (epoxy resins) as well as thermoplastic materials (engineering plastics). This monomer can provide no unsaturated bond in the structure for the enhanced properties of some modified polyesters , polycarbonate, polyurethane, polyacrylate, polysulphone, alkid under the purpose to replace target traditional engineering materials such as wood or metal. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white flakes | |
| HYDROXYL VALUE | 430 min (mgKOH/g) | |
|
Fe |
5ppm max |
|
|
ASH |
50ppm max |
|
|
COLOR |
30 max ( Hazen) |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36, Safety Phrases: 16 | ||